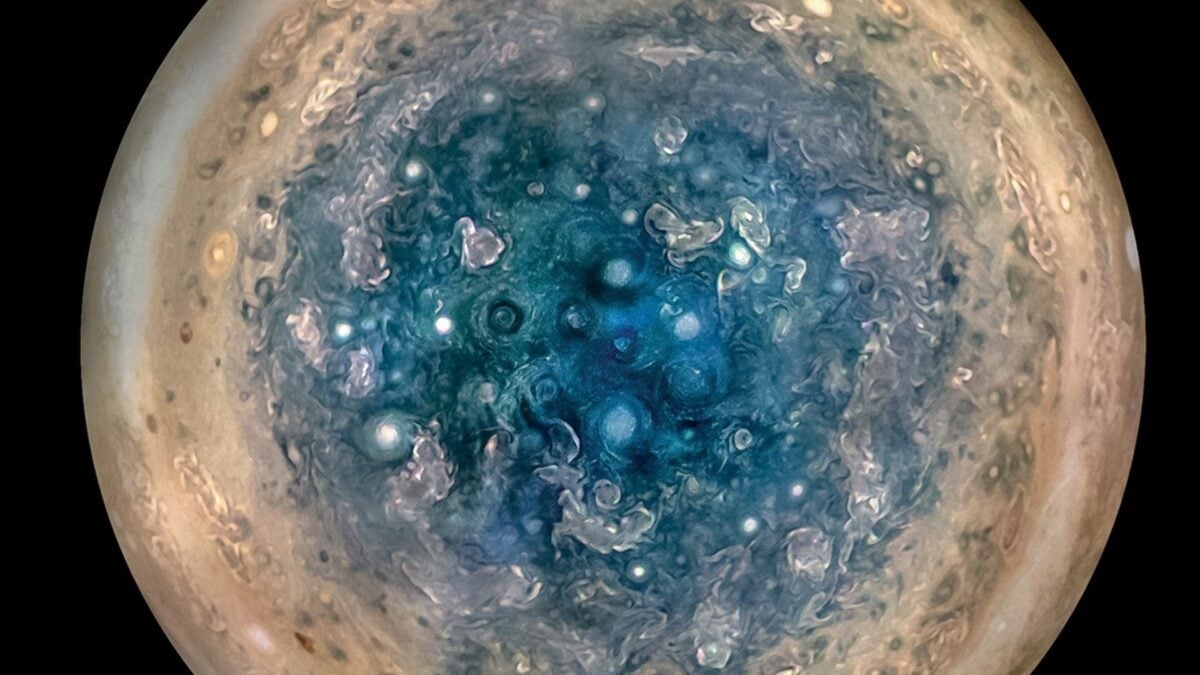
Ever since he entered Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, NASA’s spacecraft It was hard to work reveal the many mysteries from the largest planet of our solar system. And its latest discovery may be one of the most interesting yet: a completely new type of plasma wave near the bars of Jupiter.
In paper published on Wednesday in Physical review lettersAstronomers describe an unusual pattern of plasma waves in the magnetosphere of Jupiter – a magnetic “bubble” shielding the planet from external radiation. Jupiter’s exceptionally powerful magnetic field seems to force two very different types of plasmas to stick in tandem, creating a unique flow of loaded particles and atoms in its polar regions.
Plasma is a key force to form the turbulent atmosphere of Jupiter. As such, the researchers believe that the new observations will further promote our understanding of not only the weather events of Jupiter but also the magnetic properties of distant exoplanets.

For the study, the researchers analyzed the behavior of plasma waves in the magnetosphere of Jupiter containing a highly magnetized, low-density plasma. The team, collaboration between researchers from the University of Minnesota, the University of Iowa and the Southwest Research Institute, Texas, found an unexpected oscillation between Alfvén waves and langmuir waves, which reflect the movement of the atoms of the plasma and the movement of the electrons in the plasma respectively.
Electrons are much lighter than loaded atoms, which means that usually, the two wave types tear very different frequencies – which clearly did not happen for the magnetosphere of Jupiter, prompting the researchers in more detail. The following survey revealed never before seen type of plasma oscillation near the bars of Jupiter.
“The observed plasma properties are really unusual, not found before and elsewhere in our solar system,” John Leif Jørgensen, a planetary scientist from Denmark Technical University, who was not involved in the new work, said A new scientist.
Unlike the auroras of the earth, which are caused by solar storms, Auroras of Jupiter – a barge of rogue, super -fast items that are a hundred times more energetic Ol aurora on Earth – sometimes appear as a product of its powerful magnetic field. Getting a better understanding of how such phenomena could be valuable information for future missions in the pursuit of alien life on exoplanets, according to the authors of the study.
“While such conditions do not occur [on] Earth, it is possible that they apply in polar regions of the other giant planets and perhaps in strongly magnetized exoplanets or stars, “the astronomers wrote in the paper.
“Jupiter is the Rosetta stone of our solar system,” said Scott Bolton, Juno’s chief inquiry, in NASA Introduction page for the spacecraft. “Juno goes there as our express – to interpret what Jupiter has to say.”
Initially, NASA was waiting for Juno’s mission to finish in 2017, when they would deliberately lead the spacecraft into the atmosphere of Jupiter, a decision that joins NASA’s planetary protection requirements. But Juno’s flight route evolved over time, and NASA concluded that the spacecraft No longer posed a threat to the moons of Jupiter. As a result, the agency authorized extensions to the mission.
This is said, the scientists believe that by September of this year, the orbit of Juno Degelos Nature, and it will be blown up by the atmosphere of Jupiter. However, this does not end the research of the humanity of Jupiter; Europa clipper is scheduled to reach Europa, Jupiter -Moon, in 2030 (the last time we checked, it made some sights near Mars). Of course, even after Jupiter consumes Juno, scientists will still have many worthless data from the spacecraft, which they will continue to scrupulously analyze over the coming years.